Utility Monitoring Points
Utility monitoring points (UMP) are used to monitor underground utilities for potential displacements caused by construction activities. Datasheet
UMP Applications
Utility monitoring points are used to monitor underground utilities for potential displacement from excavating, dewatering, tunneling, trenching, and other construction activities.
UMPs can also serve as automated heave-settlement points to monitor ground loss or heave in foundation soils.
UMP Monitoring Options
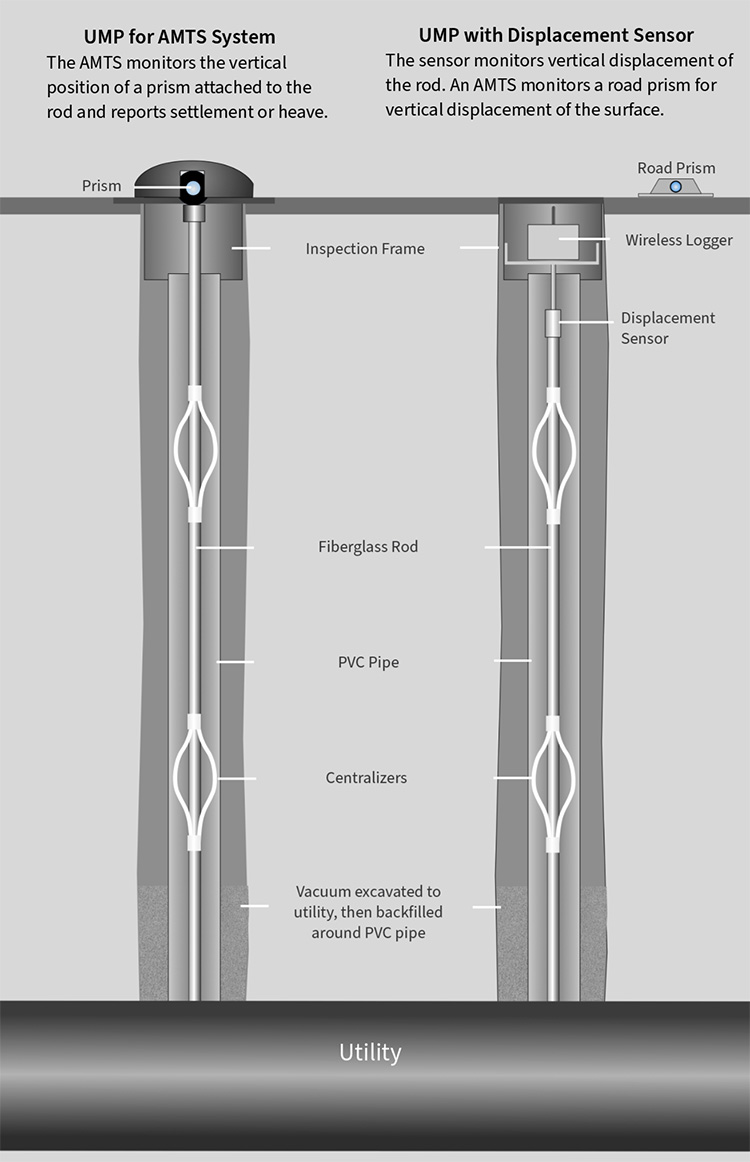
AMTS System: An AMTS monitors the vertical position of a prism attached to the top of the rod and reports settlement or heave. Above-grade prisms can be protected by a dome as illustrated. Below-grade prisms can be protected by a slotted plate.
AMTS systems can monitor multiple UMPs along with other monitoring points. The AMTS control point network provides a fixed reference for all measurements.
Displacement Sensor: The sensor monitors vertical displacement of the rod. An AMTS monitors a road prism for vertical displacement of the surface. The reported settlement or heave is the difference between surface displacement and rod displacement.
The sensor option is useful when protective domes would obstruct traffic and when there are poor sightlines to prisms under slotted covers.
GeoCloud Website: Both options forward their measurements to GeoCloud websites. Graphs, data, and reports are available 24/7.
UMP Installation
- Access to the utility is created by vacuum excavation.
- A PVC pipe is placed in contact with the utility. Backfill is placed around the pipe.
- An inspection frame is installed and the ground surface is restored.
- A solid fiberglass rod with centralizers is lowered into the PVC pipe until contact is made with the utility.
- The top of the rod is terminated with a prism or a displacement sensor.

PVC pipe in place. Utility is visible at bottom of excavation.
UMP Components

Protective dome can withstand rollovers by heavy equipment.

Slotted cover plate is a low-profile alternative for below grade prism.

UMP with sensor option & road prism. Wireless logger transmits through lid

AMTS monitoring road prism
located near a UMP.
