PhotoMonitoring
PhotoMonitoring is an AI-driven system that analyzes sequential images of slopes or structures to detect changes and quantify displacements. Datasheet
PhotoMonitoring
PhotoMonitoring™ is an AI-driven system that analyzes sequential images of slopes or structures to detect surface changes and provide metrics for displacements, strain, and cracks.
Applications
Monitoring tunnels to reveal ovaling or convergence in cross sections or vertical settlement in profile.
Monitoring slopes to reveal movement vectors and activity rates for slides, rockfalls, and other geohazards.
Monitoring structures such as dams, bridges, and buildings to reveal deformation and evolution of cracks.
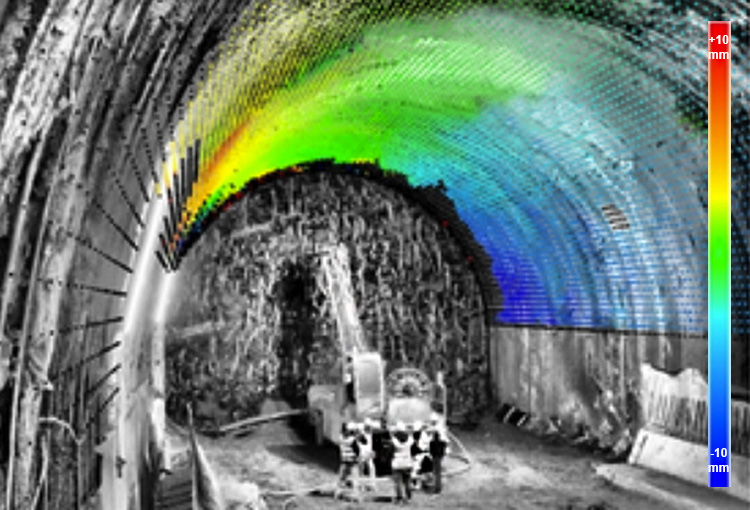
Monitoring tunnel deformation
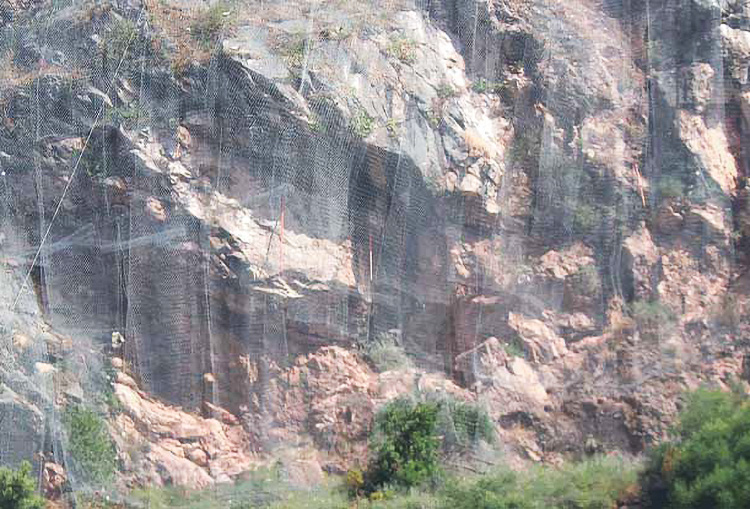

Monitoring rockfall activity
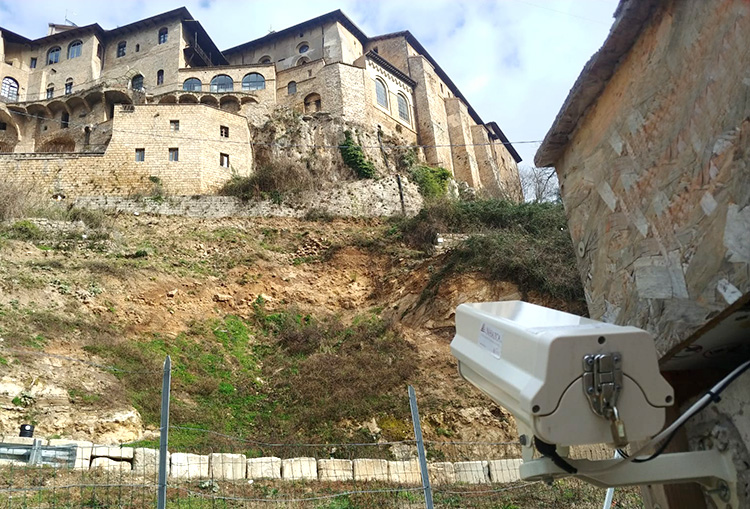

Monitoring slope stability
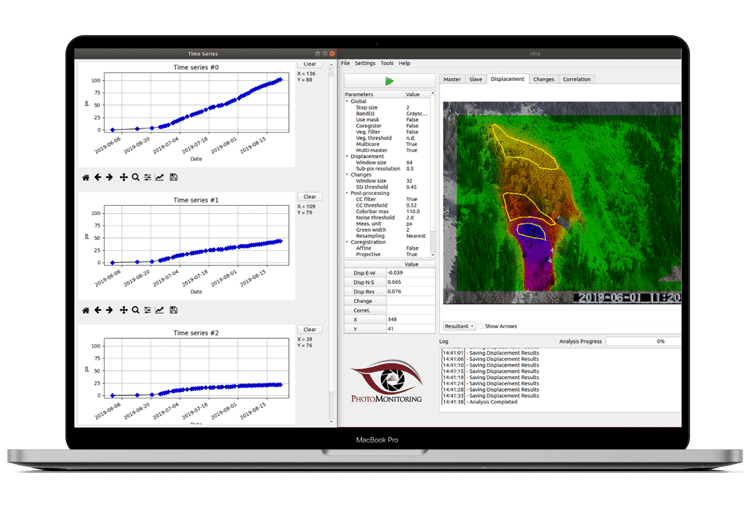
IRIS Analysis Software
Advantages
- Implemented at a lower cost than LiDAR and Radar systems.
- Provides full surface coverage with point level detail.
- Eliminates the need for installing or replacing targets or sensors.
- Can provide near-continuous monitoring and alerts.
- Provides a visual record that supplements quantitative data.
System Components
Cameras: Cameras, drones, and satellites, chosen to provide adequate resolution. A GSD tool can be used to guide selection.
Internet connectivity: Required for transmitting images to a server for processing.
IRIS Analysis Software: Processes the images, generates reports and data visualizations using algorithms developed by NHAZCA.
IRIS™ Analysis Software
- Ingests images from terrestial, aerial, and satellite cameras.
-
Aligns images to accommodate changes in camera position.
-
Corrects or filters images for changes in illumination that could interfere with analysis.
-
Filters images with excessive noise from rain, fog, and snow.
-
Elimination of objects such as construction machinery or animals.
- Identifies areas of change, calculates displacements, and outputs easily understood visualizations.
- Provides alerts with images, change maps, and data that can feed dashboards and downstream notification systems for early warnings.
Resolution
Resolution in photo monitoring is characterized along four related axes:
Spatial resolution: The area on the monitored surface that the camera records as a single pixel. For example, the pixel in the recorded image may represent an area of 3 cm x 3 cm on the monitored surface.
Temporal resolution: The sampling interval, affects rates of change calculations.
Radiometric resolution: The contrast and detectability of subtle changes influenced by bit depth and dynamic range. Important for digital image correlation or crack detection.
Measurement resolution: The smallest change in position reliably reported by image correlation, possibly a fraction of a pixel, and converted to mm or cm. Important for displacement calculations.
PhotoMonitoring and IRIS are trademarked technologies from NHAZCA s.r.l.
